
ELECTRICITY (विधुत)-Competitive Physics
Physics topic- “ELECTRICITY (विधुत)-Competitive Physics”, is important for all competitive exams like CET- Common eligibility Test, SSC CGL, SSC CHSL, RRB NTPC, UPSC and other state civil services exams. In these exams, almost 4-5 questions are coming from Physics. Let’s start the topic- ELECTRICITY (विधुत)-Competitive Physics.
ELECTRICITY (विधुत) and its Characteristics:
Electricity is a form of energy that results from the flow of charged particles. So, we can say “the continuous flow of electron is called electricity”.
Negative charges particles are called electrons and are not held very tightly in the atom so it is easy for them to move around.
There are two types of charges: 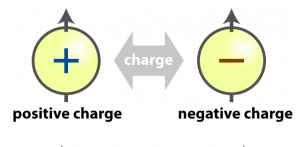
- Positive Charge is one who loosed its electrons and becomes positively charged.
- Negative Charge is one which gains electrons and becomes negatively charged.
To know more about the terms atom, electrons, protons, neutron etc. scroll down this page.
There are two type of electricity :
- Static Electricity.
- Current Electricity.
Static Electricity:-
Static electricity refers to an imbalance between the electric charges in a body, specifically the imbalance between the negative and the positive charges on a body.
- In static electricity charged particles are transferred from one body to another.
If two objects are rubbed together, especially if the objects are insulators and the surrounding air is dry, the objects acquire equal and opposite charges and an attractive force develops between them. The object that loses electrons becomes positively charged, and the other becomes negatively charged.
For example: 
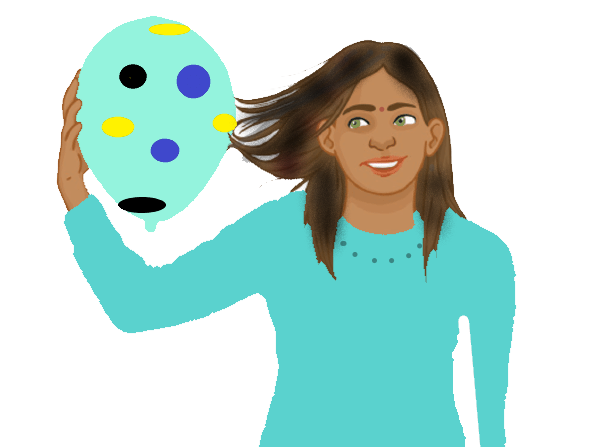
- When we rub the comb into hairs and take it near small pieces of paper, all the paper pieces get attracted towards the comb. This is because of static charge that is developed due to rubbing of comb on oily hairs.
- When we rub a balloon to our hairs, it make hair in stand up position.
- Lightning is also the result of static electricity.
How lightning occurs in sky? 
Air, water droplets, and even ice crystals rub violently against each other inside a thundercloud, creating two opposite kinds of electrical charge: negative and positive. When the attraction between charges is so strong that they push through the air towards each other, then they formed lightning in sky.
- Lightning has more than 20 million Volts.
Current Electricity: –
The movement of electrons from one point to another in an electric circuit is called current electricity. 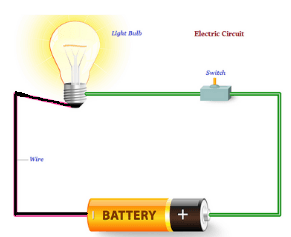
Electric circuit: A continuous and closed loop path of an electric current is known as an electric circuit. If the loop is broken anywhere, the electricity can’t get through.
Types of Current Electricity
- Direct Current (DC)
- Alternating Current (AC)
Direct Current (DC):- 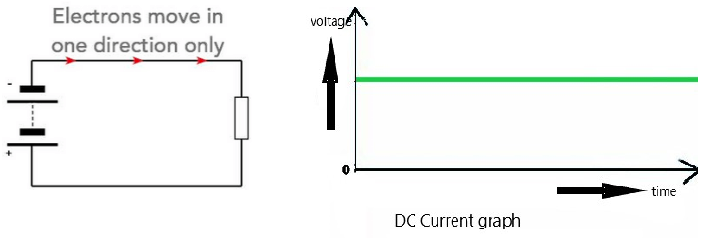
Direct current is defined by the constant flow of electrons from a region of high electron density to a region of low electron density. DC is used in many household appliance and applications that involve a battery.
- The current electricity whose direction remains the same is known as direct current.
Alternating Current (AC):- 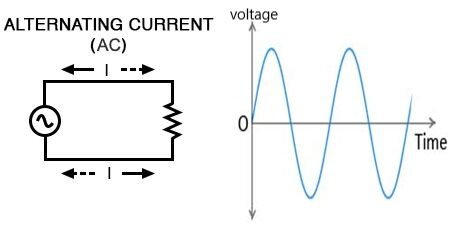
The current electricity that is bidirectional and keeps changing the direction of the charge flow is known as alternating current. Or we can say, Alternating current is a current that changes its magnitude and polarity at regular interval of time.
- The bi-directionality is caused by a sinusoidally varying current and voltage that reverses directions, creating a periodic back and forth motion for the current. The electrical outlets at our home and industries are supplied with alternating current.
Atom: The atom is the basic building block for all matter in the universe.
- An atom is composed of two regions: the nucleus, which is in the center of the atom and contains protons and neutrons, and the outer region of the atom, which holds its electrons in orbit around the nucleus.
- In an atom the number of protons and electrons are equal. Thus an atom is electrically neutral in nature.
Protons: – Protons are the positively charged particles which are present in the nucleus of an atom.
Electrons: – Negative charges particles are called electrons and are not held very tightly in the atom so it is easy for them to move around.
Neutrons: – Neutrons have no charge, they are electrically neutral. They are also present in nucleus of an atom. The number of neutrons affects the mass and the radioactivity of atom.
Nucleons: – The nucleus contains protons and neutrons which are collectively called nucleons.
Potential difference: – Potential difference is the difference in the amount of energy that charge carriers have between two points in a circuit. 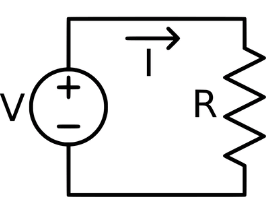
- SI unit of electric potential difference is given volt (V).
- The instrument that measures the potential difference is known as the voltmeter.
Electric Current: – The electric current is the rate of flow of electric charge through a conducting medium with respect to time.
- The charge can be negatively charged electrons or positive charge carriers including protons, positive ions or holes.
- The SI unit of electric charge is coulomb (C).
- Coulomb is equivalent to the charge contained in closely 6.24 ×(10 ‘s power 18) electrons.
- The electric current is expressed by a unit known as an ampere (A).
- The instrument that measures electric current in a circuit is known as ammeter.
- It was named after the French scientist Andre-Marie Ampere.
Electric Power: – The rate at which electric energy is dissipated or consumed in an electric circuit is known as electric power.
- The SI unit of electric power is watt (W).
ELECTRICITY (विधुत)-Competitive Physics
Ohm’s law:-  Ohm’s law states that “The electric current flowing through a metallic wire is directly proportional to the potential difference V, across its ends provided its temperature remains the same.”
Ohm’s law states that “The electric current flowing through a metallic wire is directly proportional to the potential difference V, across its ends provided its temperature remains the same.”
I ∝ V
Resistance:- Resistance is a measure of the opposition offered to the current flow in an electric circuit. 
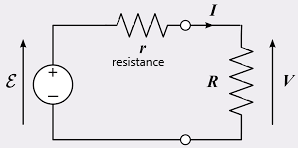
- In a circuit component or device the electrical resistance is defined as “the ratio of the voltage applied to the electric current” which flows through it.
- R = V/I
- The resistance of a conductor is directly proportional to its length (L) as R ∝ L. so, with increase in the length of conductor (wire) their resistivity also increase.
- The resistance of a conductor is inversely proportional to its cross-sectional area (A) as: R ∝ 1/A. so, when the cross–section area of wire increase, its resistance will decrease.
- The SI unit of electric resistance is the “ohm”.
ELECTRICITY (विधुत)-Competitive Physics
Electric Conductance (G):- Electric Conductance measures how easily electricity flows through electrical components for a given voltage difference.
- Electrical conductance, is the reciprocal of resistance (R):
G=1/R
- The SI unit of conductance is siemens (the older unit was the mho).
- Electrical conductance is closely related to electrical conductivity.
- Electrical conductance is a property of a particular electrical component (like a particular wire), while conductivity is a property of the material itself (like – copper).
For More:
Electricity Facts for Competitive Exam:
- Silver is the best conductor of electricity because it contain the large number of free electron.
- The speed of electricity approximate equal to the speed of light = 3 x (10’s power 8)m/sec.
- The SI unit of electric charge is coulomb (C).
- The electric current is expressed by a unit known as an ampere (A).
- The instrument that measures electric current in a circuit is known as ammeter.
- The SI unit of electric power is watt (W).
- SI unit of electric potential difference is given volt (V).
- The instrument that measures the potential difference is known as the voltmeter.
- At the time of thundering, we are safe inside the car rather than outside because car act as hollow sphere and spread charge.
- An iron chain touches road in tankers because at the time of thundering, it can neutralized the charge.
- Lighting conductor established at roof of taller buildings which are made up of copper.
- Switch are made up of “Bakelite”.
- Insulators are used in electrical poles are made up of “Muscovite”.
- Filament of and electric blub is made up of “Tungsten”.
- Glowing of blub occurs due to heating effect of electricity.
- Temperature inside the electric blub is 2000 – 2500.
- “Nichrome” is use in the manufacturing of heater coil.
- Fuse wire is made up of lead + tin.
- Fuse wire working on the principle of heating effect of electricity. They melt and break the circuit, during the short circuit.
- Transformer are made up of wrought iron.
- The most suitable metal for making electromagnets is soft iron.
- The most suitable metal for making permanent magnets is steel.
- Motor convert electrical energy into mechanical energy.
- Generator convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. It works vise-versa of motor.
- Light bulbs are filled with an inert gas like nitrogen, argon.
- Tube-light, CFL (compact fluorescent lamp), bacon lamp are filled with Neon Gas.
- CFL (compact fluorescent lamp), tube lights gives more light by consume less electricity because there wall coated with fluorescent power and mercury vapor, which convert heat energy into light.
- Parallel circuits are used in homes because the loads can be operated independently of each other.
- All domestic and electrical equipment use electricity of frequency 50 Hz.
- Mica is the bad conductor of electricity but mica is good conductor of heat. It is the reason, it is widely used in electric heating device like as cloth iron.
LCD (Liquid Crystal Display):- 
- It is a combination of two states of matter, the solid and the liquid.
- LCD uses a liquid crystal to produce a visible image. Liquid crystal displays are super-thin technology display screens.
- Use of LCD in laptop computer screens, TVs, cell phones, and portable video games.
- LCD’s technologies allow displays to be much thinner when compared to a cathode ray tube (CRT) technology.
LED (light emitting diode):-
- A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor light source that emits light when current flows through it.
- LED lighting products produce light up to 90% more efficiently than incandescent light bulbs.
Advantages of LEDs:- 
- Lower energy consumption, longer lifetime, smaller size, and faster switching.
- Made popular by their efficiency, range of color, and long lifespan.
Applications of LED:-
- LEDs uses in fairy lights, automotive headlamps, advertising, general lighting, traffic signals, camera flashes, lighted wallpaper, horticultural grow lights, and medical devices
- Including night lighting, art lighting, and outdoor lighting. These lights are also commonly used in electronics and automotive industries.
If you like and think that General Science (Physics) topic on “ELECTRICITY (विधुत)-Competitive Physics” was helpful for you, Please comment us. Your comments/suggestions would be greatly appreciated. Thank you to be here. Regards – Team SukRaj Classes.





