Mouth- Teeth, Tongue, Lips & Salivary Glands (मुखगुहा) – Biology Topic.
Topic of Biology- “Mouth or Buccal Cavity (मुखगुहा) – Teeth – Tongue – Lips – Salivary Glands”, is important for all competitive exams like SSC CGL, SSC CHSL, RRB NTPC, UPSC and for other state civil services exams. In these exams, almost 4-5 questions are coming from Biology. Let’s start the topic – Mouth or Buccal Cavity.
Mouth (Teeth, Tongue, Lips, Salivary Glands and Tonsil)
मुखगुहा – (दांत, जीभ, होंठ, लारग्रन्थी और टॉन्सिल्स)
The mouth is also called as the buccal cavity or the oral cavity. In the human digestive system mouth is the upper end or the beginning of the alimentary canal.
Parts of the Buccal Cavity:
- Lips
- Teeth
- Tongue
- Salivary glands.
- Tonsil
1. Lips (होंठ):
Lips are the soft, muscular and movable structures, which are formed by the complex of Orbicularis oris muscles.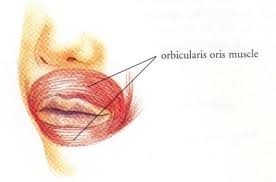
- The reddish-pink appearance of the lips is mainly because of the: Buccal-mucosa blood vessels.
Buccal-mucosa:
- It is the inner lining of the cheeks and the back of the lips.
- It provides a round shape to the cheeks.
2. Teeth (दांत):
Our teeth are one of the strongest parts of your body. They’re made from proteins such as Collagen, and minerals such as Calcium.
Teeth have three layers: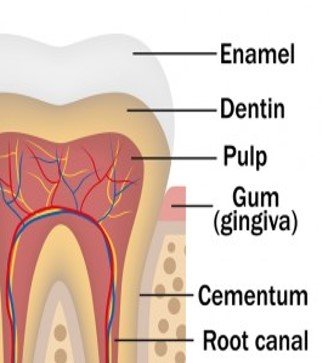
- Enamel: It is a hard protective outer layer covering the crown of the tooth.
- Dentine: It is a second protective layer covering the nerve of the tooth.
- Pulp: It (also called the nerve) is the soft middle of the tooth that has a blood supply and nerve endings.
The outermost layer of Teeth is called: Enamel. (It is also called Tooth Polish)
Enamel (एनामल): It is the hardest substance of human body. Which contain least amount of water.
Human is known as – Bi- Phydont.
- Bi – Phy- Dont = Two Times + Occurring + Teeth
Adults have 4 types teeth: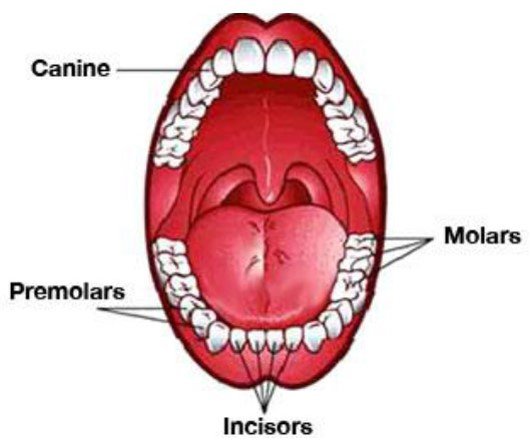
- I — Incisors — Cutting Teeth.
(8 incisor teeth are located in the front part of our mouth. We have four of them in our upper jaw and four in our lower jaw.)
- C — Canines — Tearing Teeth.
(4 canine teeth sit next to the incisors. we have two canines on the top of our mouth and two on the bottom).
- P – Premolars — Breaking Teeth.
(8- premolars sit next to your canines. There are four premolars on top and four on the bottom).
- M – Molars — Grinding Teeth.
(12 molars are your biggest and strongest teeth. You have six on the top and six on the bottom).
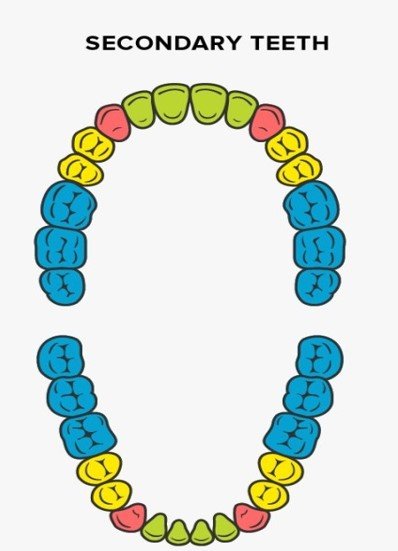
Adults have 32 teeth, called permanent or secondary teeth:
- 8 – Incisors
- 4 – Canines, also called Cuspids
- 8 – Premolars, also called Bicuspids
- 12 – Molars,(Including 4 wisdom teeth)(अकल दांत).
Children have just 20 teeth, these are first teeth called deciduous teeth or primary or temporary or milk teeth.
- 4 – Incisors
- 2 – Canines
- 4 – Molars
Milk Teeth & Adult Teeth (I C P M) {we can learn it as I SEE PM}

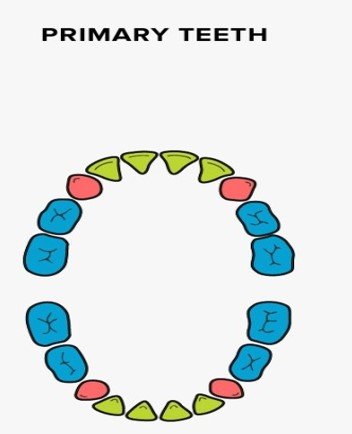
Milk Teeth (20 nos.) = { 2 1 0 2 / 2 1 0 2 } x 2
Adult Teeth (32 Nos.) = { 2 1 2 3 / 2 1 2 3 } x 2.
Note : They include the same teeth in the upper and lower jaw.
| AGE | I (Insesors) | C (Canine) | P (Premolar) | M (Molar) |
Milk Teeth | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 |
| 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | |
Adult Teeth | 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
Important Facts on Teeth for Competitive Exams:
- Study of teeth is called: Odontology.
- Physician of Teeth are called: Odontologiest.
- Enamel (एनामल): It is the hardest substance of human body.
- 12 Teeth Occurs in Human life only one time (in Whole human Life) (12 दांत जीवन में एक ही बार आते हैं )
- A human tooth has three main sections and they are the crown, neck and root.
- The crown is the visible part of your tooth you can see in your mouth.
- The neck is the part of the tooth that connects the root and crown together.
- The root is the part of the tooth that is attached to your gums.
- Premolar does not present in Milk Teeth.
- 30th to 32th teeth comes (wisdom teeth/अकल दांत) in the Age of 25 to 30 Yrs.
- The part of teeth which embedded in Jaw is called (मसूड़े में धंसा हुआ हिस्सा)– Root of Teeth
- Molar Teeth have = 3 Roots,
- Remaining Teeth have = 1 Root.
- Largest Teeth = Elephant Tusk (हाथी के आगे के दिखने वाले 2 दांत).
- Elephant Tusk = It is modification of Upper Incisors.
- Animal having one set of teeth in their life time are called —Mono-Phydont. Cow is very good example of this.
- Rat is Poly-phydont.
- Animals like the beluga whale have only one set of teeth in their lifetime.
3. Tongue (जीभ):
The tongue is a flexible and muscular sense organ in the mouth. It is covered with moist, pink tissue called mucosa. Our tongue has a soft, thin and smooth skin called mucous membrane. Tiny bumps called papillae give the tongue its rough texture. Thousands of taste buds cover the surfaces of the papillae.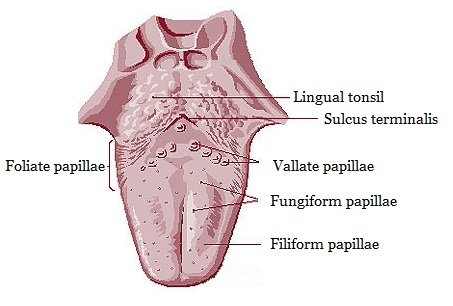
Note :
- Our tongue is fastened to the jaw bone (mandible) and to the front of our throat.
- A bright red tongue may be a sign of folic acid or B12 deficiency.
Taste buds (स्वाद कलिकाएँ):
These are collections of nerve-like cells that connect to nerves running into the brain. The tongue has many nerves that help detect and transmit taste signals to the brain. A taste bud is made up of between 50 and 150 receptor cells.
There are four common tastes are sweet, sour, bitter, and salty but there is a fifth taste also, called umami (savoury flavours) that our tongue can taste with the help of receptor cells. Because of test buds and nerves, all parts of the tongue can detect these four common tastes.
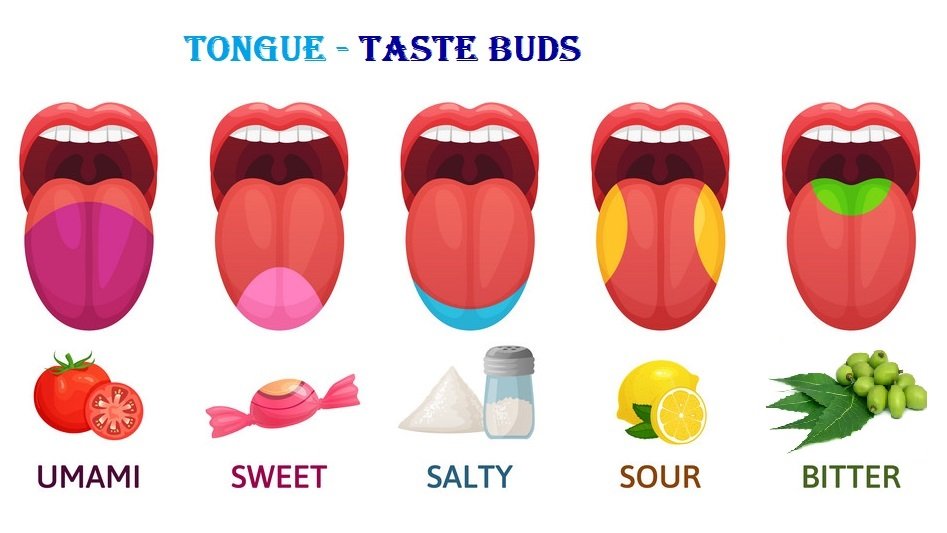
- Our tongue, has lots of ‘taste buds’ (between 2000 and 4000) (inside the papillae) for picking up different five tastes.
- The Taste Buds that sense sweet tastes are near the front of the tongue.
- The Taste Buds that sense salty tastes are in between front and middle part of the tongue.
- The Taste Buds for sour tastes are mainly along the sides of the tongue.
- The Taste Buds for bitter tastes are at the back of the tongue.
Note: The nose and the tongue work as a team for tasting the food – smell is very important to tasting foods. If our sense of smell isn’t working properly (like when you have a cold), foods can taste very – tasteless.
Important Facts on Tongue for Competitive Exams:
- The tongue is muscular sense organ that is part of the human gustatory and digestive systems.
- We feel Taste (स्वाद) due to – Taste Buds.
- Taste buds present in the papillae of tongue.
- Total no of Taste buds in human tongue are in between 2000 and 4000.
- A taste bud is made up of between 50 and 150 receptor cells.
- The receptors cells of the Tongue can taste different flavors, like bitter, salty, savory, sour and sweet.
- Front Part of the tongue, use to taste Sweet (मिट्ठा).
- Pre-middle part of the tongue, use to taste Salty (नमकीन).
- Both the sides part of the tongue, use to taste Sour (खट्टा).
- Back or end part of tongue, use to taste Bitter (कडवा).
- The tongue helps you make speak and sounds.
- The average size of an adult male tongue is 3.3 inches and an adult female tongue is 3.1 inches.
- The tongue has two groups of muscles and they are the intrinsic muscles and the extrinsic muscles.
- There are four intrinsic muscles and they allow you to change the shape of our tongue.
- There are four extrinsic muscles and they allow you to change the position of our tongue.
- The primarily blood supply for the tongue comes from the lingual artery.
- Just like our fingerprints, no two humans have the exact same tongue.
4. Salivary gland (लारग्रंथी):
It is a organ in mouth that secrete saliva (लार), a substance that moistens and softens food, into the oral cavity of vertebrates. The basic secretory units of salivary glands are clusters of cells called an Acini.
Most animals have three major pairs of salivary glands that differ in the type of secretion they produce:
- Parotid glands : It is biggest and main Slavery gland that produce a serous, watery secretion.
- Submaxillary glands: It produce a mixed serous and mucous secretion.
- Sublingual glands: It secrete a saliva that is predominantly mucous in character.
Important Facts about Salivary-Gland for Competitive Exams:
- There are 3- Pairs or 6 nos. of Salivary glands present in human Buccal Cavity.
- Parotid glands is biggest and main type of Slavery gland.
- These Salivary glands release approx. 1.5 to 2.5 litter/day Saliva.
- In Saliva there are two type of enzymes found – Ptyalin and Amylase.
- Both these enzyme are used to dissociate the Carbohydrate in to Maltose.
- Ptyalin enzymes are sometimes also called Alpha-amylase enzymes.
5. Tonsil (टॉन्सिल्स):
At the back of our mouth are tonsils.
- One is called the lingual tonsil and is at the back of your tongue.
- The other two tonsils are called palatine tonsils. We can see them when we look down our throat – they are at each side.
- Tonsils help to catch and destroy germs which try to get into our body. Sometimes there are too many germs, and the tonsils get swollen up. That’s when we get tonsillitis.
Also Read: –
For More:
If you like and think that Biology topic on “Mouth or Buccal Cavity (मुखगुहा) – Teeth – Tongue – Lips – Salivary Glands” was helpful for you, Please comment us. Your comments/suggestions would be greatly appreciated. Thank you to be here. Regards – Team SukRaj Classes.