Human Heart (मानव हृदय) – Circulatory System of Human Body – Biology
Biology topic -“Human Heart (मानव हृदय) – Circulatory System of Human Body“, is important for all competitive exams like SSC CGL, SSC CHSL, RRB NTPC, UPSC and other state civil services exams. In these exams, almost 4-5 questions are coming from Biology. Let’s start the topic: Human Heart (मानव हृदय) – Circulatory System of Human Body.
“Human Heart ( मानव हृदय) – Circulatory system of human body”
The human heart is an organ that pumps blood throughout the body via the circulatory system, supplying oxygen and nutrients to the tissues and removing carbon dioxide and other wastes.
Human Circulatory System
The Circulatory System is the system of organs which is responsible for transport of materials inside the body. It consists of heart, arteries, veins, capillaries and blood.
Shape of the heart is Triangular and is made up of special muscle called Cardiac muscle.
The heart acts as a pump to push out blood. The arteries, veins and capillaries act as pipes or tubes through which the blood flows. These tubes carries blood are called blood vessels.
So, there are three types of blood vessels in the human body:
- Arteries

- Veins
- Capillaries
- Arteries :
- Arteries are thick walled blood vessels which carry blood from the heart to all the parts of the body.
- They are thick because blood emerges from the heart under high pressure.
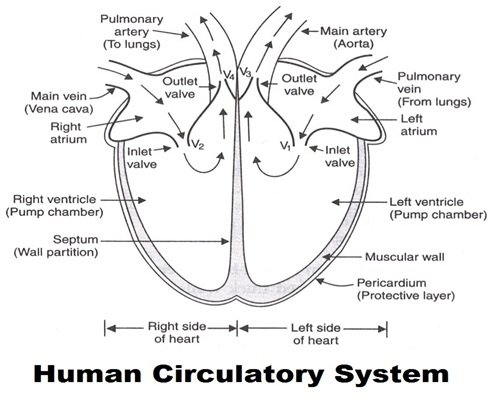
- The main artery called Aorta is connected to the left ventricle of the heart through a valve V3.
- The function of main artery is to carry oxygenated blood from left ventricle to all the parts of the body except lungs.
- Another artery called Pulmonary Artery is connected to the right ventricle of the heart through another valve V4.
- The pulmonary artery carries de-oxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
- Veins:
- Veins are the thin walled blood vessels which carry blood from all parts of the body back to the heart. Veins do not need thick walls because the blood flowing through them is no longer under high pressure.
- The main difference between artery and vein is that an artery carries blood from the heart to the body organs whereas a vein carries blood from the body organs back to the heart.
- The blood which carries oxygen is called oxygenated blood and the blood which does not carry oxygen is called de-oxygenated blood, however carries carbon dioxide in it.

- Capillaries:
- The Capillaries are thin walled and extremely narrow tubes or blood vessels which connect arteries to veins. Thus, the exchange of various materials like oxygen, food, carbon dioxide etc. between the blood and the body cells takes place through capillaries only.
- The other end of capillaries is joined to some wider tubes called veins. The de-oxygenated blood or dirty blood coming from the capillaries enters in to veins.
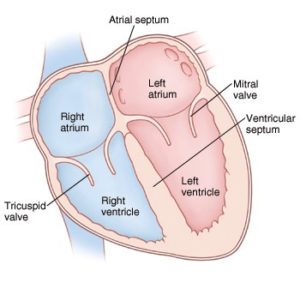
Parts Of Human Hearts:
- The heart has four compartments known as ‘Chambers’ inside it.
- The upper two chambers of heart are known as Atrium and the lower two chambers of heart are called Ventricles.
- The right atrium and right ventricle together make up the “Right heart,”
- The left atrium and left ventricle make up the “Left heart.”
- A wall of muscle called the Septum separates the two sides of the heart.
- Valves prevent back flow, keeping the blood flowing in one direction through the heart.

Human Heart (मानव हृदय) – Circulatory System of Human Body
Working of the Human Heart:
- The Pulmonary Vein brings the oxygenated blood from the lungs in to the Left Atrium of the heart, when the muscles of all the four chambers of the heart are relaxed.
- When the Left Atrium contracts, the oxygenated blood is pushed in to the Left Ventricle through the valve V1.
- When the Left Ventricle contracts, the oxygenated blood is forced in to the main Artery called ‘Aorta’.
- The main Artery carries blood to all the organs of the body like head, chest, arms, stomach, intestines etc. In this way the cells of the body gets oxygen from capillaries and then blood becomes de-oxygenated by losing oxygen.
- Now the de-oxygenated blood from the body organs enters in to the main Vein called Vena cava. The main vein carries the de-oxygenated blood to the right Atrium of the heart.
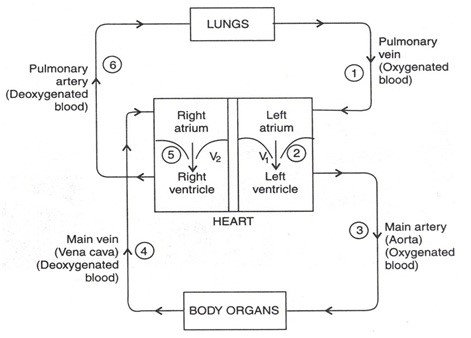
- When the Right Atrium contracts, de-oxygenated blood is pushed in to the Right Ventricle through the valve V2.
- And when the Right Ventricle contract, the de-oxygenated blood is pumped in to the Lungs through the Pulmonary Artery. In the lungs, de-oxygenated blood releases its carbon dioxide and absorbs fresh oxygen from air. So, the blood becomes oxygenated again.
- This oxygenated blood is again sent to the Left Atrium of heart by pulmonary vein for circulation in the body.
- This whole process is repeated continuously.
In human circulatory system the pathway of blood from the Heart to the Lungs and back to the heart is called Pulmonary Circulation and the pathway of blood from the Heart to rest of the body and back to the Heart is called Systemic Circulation and these two together make Double Circulation.
Heart Beats:
- One complete contraction and relaxation of the heart is called a heartbeat. The heart beat usually beats about 70 to 72 times in a minute when we are resting.
- A Stethoscope is an apparatus due to listens/ measure our heart beat.
Blood Pressure:
- The pressure at which blood is pumped around the body by the heart is called Blood Pressure.
- The maximum pressure at which the blood leaves the heart through the main artery during contraction phase is called the Systolic pressure and the minimum pressure in the arteries during the relaxation phase of heart is called Diastolic pressure.
- Systolic pressure: 120 mm Hg
- Diastolic pressure: 80 mm Hg
- So, the normal blood pressure is 120/80 and is measured by an instrument called Sphygmomanometer.
Human Heart (मानव हृदय) – Circulatory System of Human Body
Important Facts about Human Heart:-
- The heart is located in the center of the chest, usually pointing slightly left.
- All Mammals have 4- Chambered Heart.
- Due to Presence of 4 Chambered of heart, Double Circulation action of Blood takes place in Mammals: – It means pure blood and impure blood flow separately. Due to This all Mammals body temperature is constant.
- Only Crocodile Species is exception that has 4- chambered heart but it is not a Mammal.
- Goat has Maximum body temperature among the all mammals’ species.
- Human Body P.H. 4 to 8.4 (Slightly Alkaline).
- Heart, is also protected with Double Membrane layer known as Pericardium.
- Sound of Heart is : Luf –Duf.
- Heart beat of human heart is = 72 times/Min. and Measured with —Stethoscope.
- Instrument by which Blood Pressure is measured – Sphygmomanometer.
- Blood pressure value of a healthy body is = 120/80.
- 120 — (Upper range of B.P.) —is called — Systolic Pressure.
- 80—(Lower range)—is called – Diastolic Pressure.
- Adrenaline Hormone controls the Blood Pressure.
- Heart – Murmur – Disease takes place due to Leakage of Heart Valve.
- Sino-auricular Node (S.A Node) — It Generate due to weeping of child at the time of birth. It is Pace-Maker of Human Heart, so it is also called “Heart Battery.”
- Heart Attack– Occur due to Inadequate Supply of the blood (Due to cholesterol deposition in veins and nerves.) A heart attack is a serious condition in which an artery that is supplying blood to your heart becomes blocked.
- At the time of Heart- Attack a Pain Takes Place, is called—- Angina Pain.
- The heart weighs between about 10 to 12 ounces (280 to 340 grams) in men and 8 to 10 ounces (230 to 280 grams) in women.
- The heart pumps about 5.7 liters of blood throughout the body.
- The left atria chamber brings in oxygenated blood from the lungs, while the right atria chamber brings in de-oxygenated blood from the vena cava veins.
- The left ventricle chamber pumps oxygenated blood into the circulatory system, while the right ventricle chamber pumps de-oxygenated blood into the lungs.
- The human heart beats around 100,000 times a day or pumping around 2,000 gallons of blood per day.
- Our heart rate, also known as your pulse, is how many times your heart beats per minute.
- When a doctor or nurse checks your pulse, they’re checking your current bpm.
- “bpm” stands for beats per minute. This is how many times your heart beats in a 60 second period.
- The resting heart rate of an average adult is between 60 to 100 bpm.
- The resting heart rate of an infant can be up to 129 bpm.
- The study of heart disorders and diseases is called Cardiology, and someone who studies cardiology is called a Cardiologist.
- Heart Transplantation (cardiac transplant) is when the heart from one human (organ donor) is removed and surgically placed into another human (transplant recipient).
Click Here For more:
If you like and think that topic “Human Heart (मानव हृदय) – Circulatory System of Human Body” was helpful for you, Please comment us. Your comments/suggestions would be greatly appreciated. Thank you to be here. Regards – Team SukRaj Classes.