
Sound (ध्वनि) – Competitive Physics
Competitive Physics topic- “Sound (ध्वनि)”-, is important for all competitive exams like CET- Common eligibility Test, SSC CGL, SSC CHSL, RRB NTPC, UPSC and other state civil services exams. In these exams, almost 4-5 questions are coming from Physics. Let’s start the topic- Sound (ध्वनि).
Sound (ध्वनि):
Sound is a longitudinal, mechanical wave that propagates through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid.
- Sound can travel through any medium, but it cannot travel through vacuum. There is no sound in outer space.
- Sound is a form of energy like light energy and heat energy.
- Sound is a wave made of vibrations in the air. These vibrations create sound waves which move through mediums which can be solid, liquid, or gas, before reaching our ears.
- S.I. Unit of intensity of sound is Decibel.
Medium: Sound is produced by vibrating objects. The matter or substance through which sound is transmitted is called a medium. It can be solid, liquid or gas. Sound moves through a medium from the point of generation to the listener.
Longitudinal wave: A wave in which the particles of the medium vibrate back and forth in the same direction in which the wave is moving. Medium can be solid, liquid or gases. Therefore, sound waves are longitudinal waves.
Mechanical wave: Sound waves are characterized by the motion of particles in the medium (solid, liquid, gas) Hence, they are called mechanical waves.
Important facts about Sound – for Competitive exams:
- Speed of sound approximately 332 m/sec in air at 25°C
- Speed of sound increases with temperature.
- Speed of sound ∝ temperature.
- At 1°C temperature rise, speed of sound rise from 0.61 m/sec.
- Speed of sound ∝ Humidity.
- So, humidity increase with increase the speed of sound.
- So, sound of horns (siren) can hear from very far distance in rainy season.
- As with any wave the speed of sound depends on the medium in which it is propagating.
- Sound generally travels faster in order – solids, liquids than in gases and no propagation of sound in vacuum.
- Frequencies from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz are audible sound frequency.
- Sound with a frequency below 20 Hz is known as an infrasonic sound.
- Sound with a frequency above 20,000 Hz is known as an Ultrasonic sound.
- The speed of sound is faster in materials that have some stiffness like steel and slower in softer materials like rubber.
- Factors affecting the speed of sound in air.
- The speed of sound in air is nearly the same for all frequencies and amplitudes.
- Sound is a variation in pressure. A region of increased pressure on a sound wave is called a compression (or condensation). A region of decreased pressure on a sound wave is called a rarefaction (or dilation).
- I. Unit of intensity of sound is Decibel.
- Upto 85 decibel sound is called Percival sound.
- sounds above 85 dB are harmful
- Normal conversation is about 60 dB
- The intensity of sound measured by Audio – meter.
- Sound wave cannot be polarized, while light wave can be polarized.
- Quality of sound is called pitch.
- There are two type of pitch: high pitch, low pitch.
- Reflection of sound is called “Echo”.
- Minimum distance to produce echo is approximate 17 meter or 56 feet.
- Among all gases, maximum speed of sound in “Hydrogen” (1100 m/sec).
- Among all metals maximum speed of sound in “aluminum” (6200 m/sec).
- Among all alloys maximum speed of sound in “Brass”(7200 – 8000 m/sec).
- Microphone: – Microphone convert sound wave into electrical energy or wave.
- Speaker/ loud – speaker: It convert electrical wave into sound wave.
- The use of microphone and speaker in telephone and mobile, which has two parts are ear piece – which convert electrical wave into sound wave, and mouth piece – which convert sound wave into electrical wave.
- Amplifier: – amplifier increase the amplitude of sound wave.
- The tape of tape recorder cassette consists of a thin plastic base material, and bonded to this base is a coating of ferric oxide powder.
CHARACTERISTICS OF A SOUND WAVE: 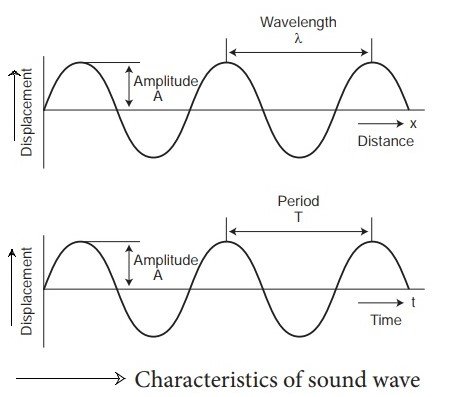
- Wavelength
- Frequency
- Amplitude
- Time period
- Velocity
Wavelength of sound: The minimum distance in which a sound wave repeats itself is called its wavelength. It is the length of one complete wave. It is denoted by a Greek letter λ (lambda).
The S.I unit for measuring wavelength is metre (m).
Amplitude: The maximum displacement of a vibrating particle from its mean or equilibrium position is called its amplitude.
- In sound, amplitude refers to the magnitude of compression and expansion experienced by the medium the sound wave is travelling through. This amplitude is perceived by our ears as loudness. High amplitude is equivalent to loud sounds.
Frequency: Frequency in a sound wave refers to the rate of the vibration of the sound travelling through the air. In sound, the frequency is also known as Pitch. The frequency of the vibrating source of sound is calculated in cycles per second. 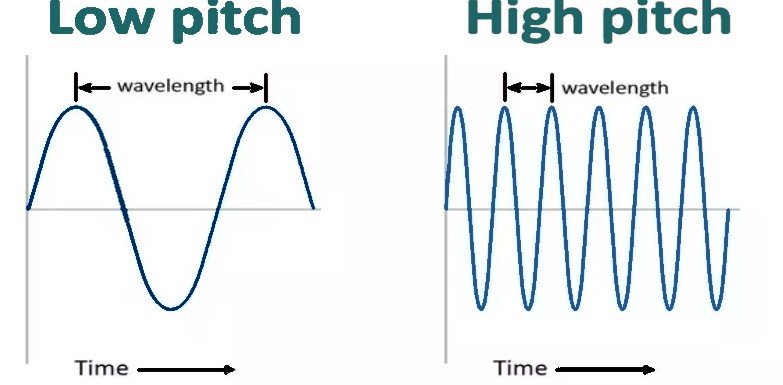
- A higher frequency sound has a higher pitch and a lower frequency sound has a lower pitch.
- The human ear can detect a wide range of frequencies.
- Frequencies from 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz are audible to the human ear.
- Any sound with a frequency below 20 Hz is known as an infrasonic sound
- Any sound with a frequency above 20,000 Hz is known as an Ultrasonic sound.
The frequency of a wave is denoted by the letter f.
F = 1/Time-period
f = 1/T
Where, (f = frequency of the wave, T = time-period of the wave)
Sound (ध्वनि)-Competitive Physics
Infrasonic sounds: Sounds of frequencies less than 20 Hz are called infrasonic sounds.
Ultrasonic sounds: The sounds of frequencies greater than 20,000 Hz are called ultrasonic sounds.
Time Period: – The time period is almost the opposite of the frequency. It is the time required to produce a single complete wave, or cycle. Each vibration of the vibrating body producing the sound is equal to a wave. It is denoted by letter T.
- The unit of measurement of time-period is second (s).
Velocity: – The velocity of the wave, sometimes referred to as the speed, is the amount of distance in meters per second that a wave travels in one second.
- It is represented by the letter v.
- The S.I unit for measuring the velocity is metres per second (m/s or ms-1).
Relationship between Velocity, Frequency and Wavelength of a Wave:
v = f X λ (Velocity of a wave = Frequency X Wavelength)
- This formula is known as wave equation.
- Where, (v = velocity of the wave, f = frequency, λ = wavelength)
Lists the ranges of sound to listen:-
| Lower frequency(Hz) | Upper frequency (Hz) | |
| Humans | 2o | 20,000 |
| Dogs | 50 | 45,000 |
| Cats | 45 | 85,000 |
| Elephants | 5 | 10000 |
| Dolphins | 0.25 | 200000 |
| Bats | 20 | 120000 |
Sound (ध्वनि)-Competitive Physics
ECO: Repetition of sound produced by the reflection of sound waves from a buildings, wall, mountain, or other obstructing surface is called echo. 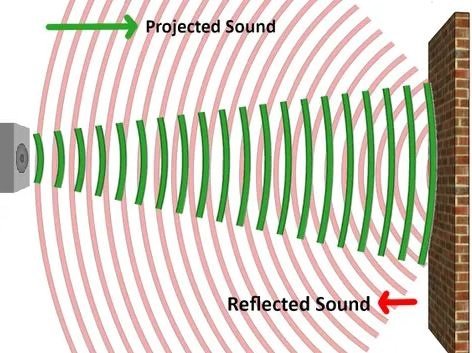
- Reflection of Sound Waves – The bouncing back of the sound wave on striking a surface such as a wall, metal sheet, plywood, etc., is called the reflection of the sound wave.
- Reverberation – If the distance is less than 17 m, then the original sound mixes with the reflected sound. Due to repeated reflections at the reflecting surface, the sound gets prolonged. This effect is known as reverberation.
Conditions for hearing the echo:
- An echo is heard only if the distance between the person producing the sound and the rigid obstacle (or reflector) is long enough to allow the reflected sound to reach the person at least 0.1 seconds after the original sound is heard
- The minimum distance in air between the source of sound and the reflector must be 17 m
- The size of the reflector must be large enough as compared to the wavelength of sound wave.
- The intensity of sound should be sufficient so that the reflected sound reaching the ear is audible
Uses of echo:
- Echoes are used by bats, dolphins and fisherman to detect an object/ obstruction.
- They are also used in SONAR (Sound navigation and ranging) and RADAR (Radio detection and ranging) to detect an obstacle.
- Echoes use in Medical such as in ultrasonography echo cardiography.
Resonance:
Resonance is a phenomenon in which an external force or a vibrating system forces another system around it to vibrate with greater amplitude at a specified frequency of operation. 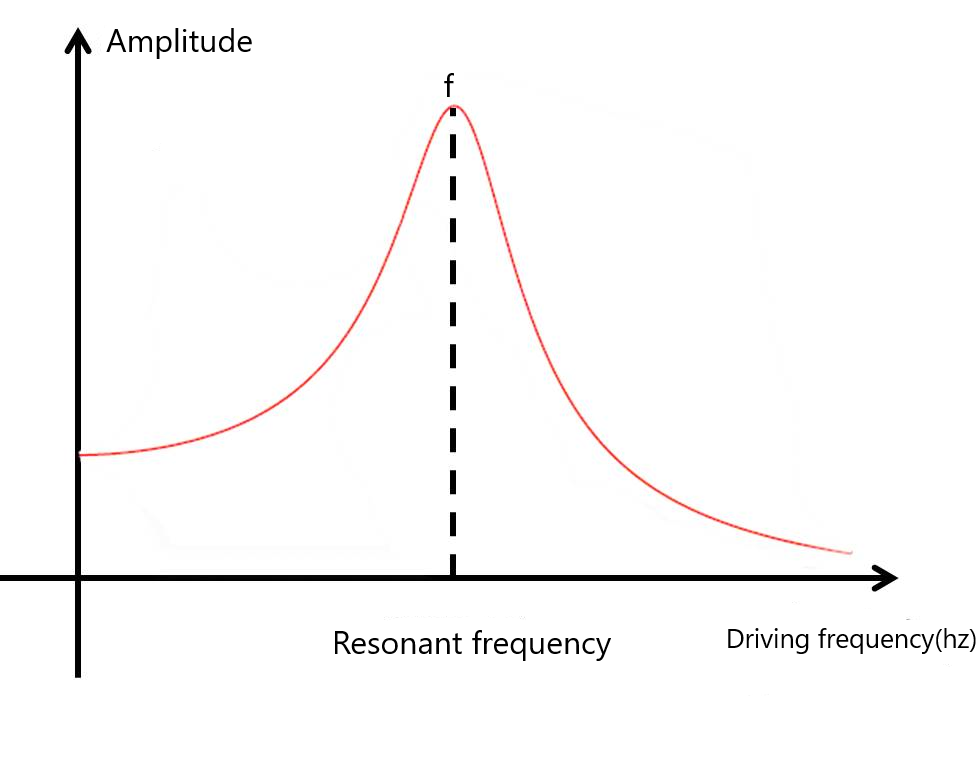
Examples of resonance:
- Bridge: – When a group of soldiers cross any bridge during marching, they are asked to break their steps because their rhythmic marching can set extreme vibrations at the bridge’s natural frequency. If the synchronized footsteps resonate with the natural frequency of the bridge, the bridge can break apart.
- Radio and T.V: – In Radio and T.V. when we change the channel, it is virtually changing the resonance frequency of tuned circuit.
- Musical Instruments: – At the time of thundering and lighting, all tight guitars, dhol, drums, tabla etc. goes breakdown due to resonance frequency.
Match number: – It is the ratio of the speed of an object to the speed of sound in the surrounding medium.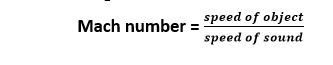
- If the Mach number is < 1, the flow speed is lower than the speed of sound – and the speed is subsonic.
- If the Mach number is ~ 1, the flow speed is approximately like the speed of sound – and the speed is transonic.
- If the Mach number is > 1, the flow speed is higher than the speed of sound – and the speed is supersonic.
- If the Mach number is >> 1, the flow speed is much higher than the speed of sound – and the speed is hypersonic.
For More:
If you like and think that General Science (Physics) topic on “Sound (ध्वनि)-Competitive Physics” was helpful for you, Please comment us. Your comments/suggestions would be greatly appreciated. Thank you to be here. Regards – Team SukRaj Classes.





