Radioactivity and Nuclear Chemistry
“Radioactivity and Nuclear Chemistry” is important for all competitive exams like CET- Common eligibility Test, SSC CGL, SSC CHSL, RRB NTPC, UPSC and other state PCS Exams. In these exams, almost 4-5 Questions are coming from Chemistry. Lets start the Topic- Radioactivity and Nuclear Chemistry.
Radioactivity and Nuclear Chemistry
Nuclear chemistry is a branch of chemistry science which deals with the study of changes in the nucleus of atoms of elements.
- These nuclear changes are a source of nuclear power and radioactivity.
- Nuclear chemistry is also termed as radiochemistry.
- It is also deals with the study of composition of atomic nucleus, nuclear forces, nuclear reactions and radioactive materials.
Nucleons:- The nucleus contains protons and neutrons which are collectively called nucleons.
Nuclear forces:– Forces binding protons and neutrons in the nucleus, are called nuclear forces.
Nuclear Reaction:-
A nuclear reaction is one in which a nucleus bombarded with an elementary particle (like neutron, proton, etc.) or with another nucleus to produce other products in a very short time span.
- The First nuclear reaction was discovered by Rutherford in 1919, when he bombarded nitrogen with alpha particles.
Radioactivity:-
Radioactivity is the phenomenon of the spontaneous disintegration of unstable atomic nuclei to atomic nuclei to form more energetically stable atomic nuclei.
- It was discovered by “Henri Becquerel” in 1895. However, term radioactivity was given by “Madam Curie”
- The SI unit of radioactivity is becquerel (Bq)
- Other Radioactivity Units: Curie, Becquerel, Rutherford.
- 1 Curie = 7×1010 radioactive decays per second.
- 1 Becquerel = 1 radioactive decay per second = 703×10-11 Ci.
- 1 Rutherford = 1.106 radionuclide decays per second.
Types of Radioactive Radiations:-
There are three types of radioactive radiations. These radiations were sorted out by Rutherford in 1902 by passing them between two oppositely charged plates.
- Those radiations which bent towards negative plate, carries positive charge are known as “alpha rays”.
- Those radiations which bent towards the positive plate, carries negative charge are known as “beta rays”.
- The third type being uncharged passed straight through the electric field are known as “gamma rays”.
Alpha Radiation
It is the emission of an alpha particle from an atom’s nucleus when an atom goes through radioactive decay.
- An alpha particle contains two protons and two neutrons and is the same as a helium nucleus.
- It is symbolized by the Greek letter α.
Beta Radiation
A beta particle is an electron ejected from the nucleus.
- It is symbolized by the Greek letter β.
Gamma Radiation
- Gamma radiation does not consist of any particles.
- It involves the emission of electromagnetic energy from an atom’s nucleus. During gamma radiation, no particles are emitted and thus it does not cause the transmutation of atoms.
- It is symbolized by the Greek letter γ.
- Most penetration power of radiation: Gama rays > Alpha rays > Beta rays.
- γ > α > β
- Most commonly emitted radio-active rays are – β rays
Stimulated Nuclear Reactions
Most of the elements undergo radioactive decay naturally While nuclear reactions can be stimulated artificially. Such types of reactions are mentioned below:-
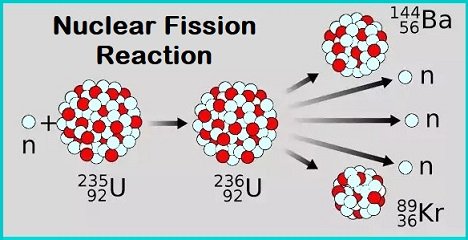
What is Nuclear Fission? 
It is the type of reaction where the heavy atom’s nucleus splits (breaks) into smaller parts, releasing a huge amount of energy in the process.
- The fission of heavy elements is an exothermic reaction, and huge amounts of energy are released in the process.
- Fission is the radioactive process used in nuclear power plants and one type of nuclear bomb.
Type of Nuclear Fission:-
Controlled Nuclear Fission
- It carried out in nuclear reactors in which rate of fission reaction is reduced and energy produced can be used for constructive purposes (such as electricity generation).
Uncontrolled Nuclear Fission
- In an atom bomb uncontrolled nuclear fission takes place.
- A very large amount of heat is produced and the process continues until the entire amount of fissionable material is exhausted.
- Nuclear fission was discovered 1938 by physicists Otto Robert Frisch, Otto Hahn, Fritz Strassman and Lise Meitner.
- Uranium-235 undergoes spontaneous fission to a small extent.
1st Atom-Bomb:
- On August 6, 1945 an atom bomb was dropped on Hiroshima city in Japan.
- Polonium was used in this bomb.
- Name of that atom bomb was ‘Little Boy’.
- At that time president of America was “Harry S. Truman”.
- That bomb was dropped by the American bomber “Enola Gay”.
2ndAtom-Bomb:
- The second atom bomb was dropped on Nagasaki, another city of Japan on August 9, 1945.
- The bomb was made of plutonium-239.
- The bomb was known as name “Fat Man“.
Note:- “Robert Oppenheimer” known as father of the Atomic Bomb.
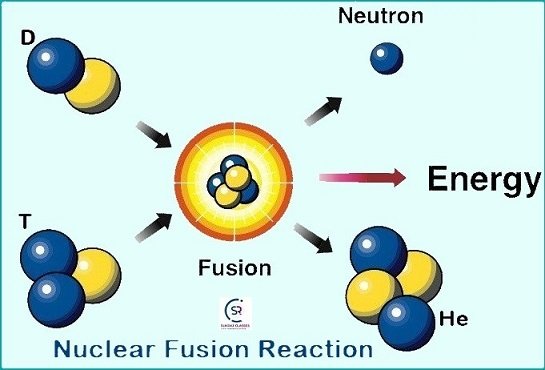
What is Nuclear Fusion? 
- It is a type of reaction where two or more nuclei of elements combined (fuse) together to form a heavier and more stable nucleus.
- Nuclear Fusion generates a large amount of energy, which is the source of power for the sun and all the stars.
- Examples: deuterium-deuterium (D-D) fusion, deuterium-tritium (D-T) fusion.
Atomic Energy (Nuclear Energy)
- Energy produced by nuclear fission or nuclear fusion is called nuclear energy or atomic energy.
- In nuclear reactions there is loss of mass. This mass is converted into energy. It can be transformed into electrical and mechanical energy which can be used for various purposes.
Nuclear Reactor:
- A nuclear reactor, formerly known as an atomic pile, is a device used to initiate and control a fission nuclear chain reaction or nuclear fusion reactions.
- Nuclear reactors are used at nuclear power plants for electricity generation and in nuclear marine propulsion.
- Nuclear reactors are the heart of a nuclear power plant.
- Chicago Pile 1 was the world’s first nuclear reactor, built in 1942 by Nobel Prize winner Enrico Fermi. The reactor was built underneath the University of Chicago’s Stagg Field football stadium.
- First nuclear reactor not only in India but also in the whole of Asia. On 4th August, 1956, the APSARA reactor.
- It is also known as “swimming pool nuclear reactor” because heavy water is use in it.
- “Tokamak” is a special type of nuclear reactor in which nuclear fusion reaction carried out.
- “ADITYA” is the first built tokamak of the India which is establish in Gandhinagar in Gujrat. It was commissioned in 1989.
Note:- Father of India’s Nuclear Programme – “Dr. Homi Jehangir Bhabha”.
Enrichment of Nuclear fuel:
- Uranium found in nature consists largely of two isotopes, U-235 and U-238.
- Both U235 and U238 are mixed in a nuclear-rod to form a fuel, is called enrichment of nuclear fuel.
Moderator:
The moderator of a nuclear reactor is a substance that slows neutrons down.
- Graphite and Heavy water is use in the nuclear reactor as a moderator.
Controller:-
A rod, plate, or tube containing a material such as boron, cadmium, silver, or indium etc., used to control the power of a nuclear reactor. By absorbing neutrons, a control rod prevents the neutrons from causing further fissions.
Note:- Liquid sodium used as a “coolant” in nuclear reactor, which transfer heat from nuclear reactor to boiler.
Geiger Muller Counter (GM Counter):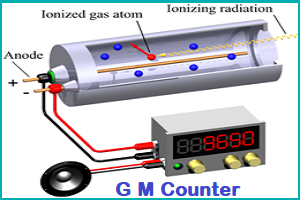
- A Geiger counter (Geiger-Muller tube) is a device used for the detection and measurement of all types of radiation: alpha, beta and gamma radiation.
- A Geiger-Müller counter can count individual particles at rates up to about 10,000 per second
- It is used widely in medicine and in prospecting for radioactive ores.
Scintillation Counter:
- Scintillation Counter is an instrument that is used for measuring ionizing radiation. A scintillation counter is used to detect gamma rays.
Cyclotron:
- A cyclotron is a machine that accelerates charged particles or ions to high energies. Both electric and magnetic fields are used in the cyclotron to increase the energy of the charged particles.
Endothermic Reaction:
- A reaction that the system absorbs the energy from its surrounding in the form of heat.
- Examples: photosynthesis, evaporating liquids, melting ice, dry ice etc.
Exothermic Reaction:
- The exothermic reaction is opposite of an endothermic reaction.
- It releases energy by light or heat to its surrounding.
- Examples: Rusting iron, settling, chemical bonds, explosions, nuclear fission etc.
Applications of Radioactivity and Nuclear Chemistry
Medicine
- MRI scans, CT scans, and X-rays for diagnosis.
- Cobalt-60 (60Co) has been used for radiotherapy cancer
- Radioactive Iodine is used for the treatment of cancers.
- Sterilization of medical instruments.
Industry
- Carbon dating.
- Radioactive tracers find use in industrial processes.
- Inspection of instruments.
Consumer products
- Smoke detectors.
- Non- sticky materials.
Food
- Food irradiation with gamma rays to prevent spoilage and enhance shelf-life.
- Pest control.
Transport
- Nuclear-powered submarines and ships.
- Radioisotope thermal generators for electricity production.
Agriculture
- Plant mutation breeding to achieve improved nutrition and food security.
- Management of fertilizer use through Radiolabeling.
- Controlling insect populations.
Radioactivity and Nuclear Chemistry
Important Facts of Radioactivity and Nuclear Chemistry for Competitive Exams: –
- Those elements which have atomic number greater than Uranium (92) are called radioactive elements.
- Radioactive elements with atomic numbers greater than 92, is the atomic number of uranium, are also called Trans-uranium elements.
- None of these radioactive elements is stable and each of them decays radioactively into other elements.
- Cobalt-60 (60Co) has been used for radiotherapy cancer
- Radioactive iodine has been used successfully for the treatment of cancer of the thyroid.
- Iodine -131 is used to treat thyroid cancer.
- Sodium 22 and sodium 24 are two radioactive isotopes of sodium.
- Sodium 24 is used as an electrolyte tracer to follow the path sodium takes in a person’s body.
- Redon is only inert-gas which is radioactive in nature.
- Francium is only radioactive liquid. It is one of the least electronegative element.
- Radioactive isotopes are used in tracing of leakage in gas and oil pipeline.
- Radioactive isotopes are also use in to determine the defects in satellite.
- Radioactive isotopes are also use in radiometric scale, by the use of this scale we can estimate the age of stones, rocks and minerals.
For More:
If you like and think that General Science (Chemistry) topic on “Radioactivity and Nuclear Chemistry” was helpful for you, Please comment us. Your comments/suggestions would be greatly appreciated. Thank you to be here. Regards – Team SukRaj Classes.