Muscles in Human Body/ Muscular System (मानव शरीर में मासपेशियाँ)
General Science – Biology topic – “Muscles in Human Body/ Muscular System (मानव शरीर में मासपेशियाँ)”, is important for all competitive exams like SSC CGL, SSC CHSL, RRB NTPC, UPSC and other state civil services exams. In these exams, almost 4-5 questions are coming from Biology. Let’s start the topic:- Muscles in Human Body/ Muscular System (मानव शरीर में मासपेशियाँ)
Muscles in Human Body
(मानव शरीर में मासपेशियाँ)
Study of Muscles/ Muscular system is called: – Myology.
Note: don’t confuse with – Mycology (Study of fungus)
Muscles: Muscles move the different parts of our body. All movement in the body is controlled by muscles. Muscles are made of fibers. Each fiber is made up of long thin cells which are packed in bundles. Each bundle is wrapped in a thin skin called perimysium. The fibers have two kinds of protein, Myosin and Actin. Some muscles work without us thinking i.e. – our heart beat, while other muscles are controlled by our brain. There are over 650 muscles in the human body. They are under our skin and cover our bones. Muscles often work together to help us move.
- Each muscle has lots of these bundles
- A bigger the muscle contains the more bundles of fibers.
- Inside the muscles there are nerves which carry messages to and from the brain.
- There are also blood vessels, which carry the energy that your muscles need and also carry away waste that your muscles have finished with.
How Muscles Work
- Muscles have long, thin cells that are grouped into bundles. Muscles work by contracting and relaxing. Contracting means becoming shorter. The muscle fibers slide together and stack up to make a fatter shape. Relaxing means the fibers slide apart and the muscle gets longer and thinner.
- When a muscle fiber gets a signal from its nerve, proteins and chemicals release energy to either contract the muscle or relax it. When the muscle contracts, this pulls the bones it’s connected to closer together.
- Many of our muscles come in pairs. An example of this is the biceps and triceps in our arms. When the biceps contract the triceps will relax, this allows our arm to bend. When we want to straighten our arm back out, the biceps will relax and the triceps will contract. Muscle pairs allow us to move back and forth.

Shapes of Muscles
Muscles come in four different shapes.
- Flat muscles: for example: in our diaphragm and in our forehead.
- Triangular muscles: for example: at the top of our arm near shoulder. This helps to pull our arm up
- Circular muscles: These muscles also called ring-shaped muscles, for examples: around the mouth, around the pupils of the eyes and also the anus so urine or bowel motions do not get out except when you want them to.
- Spindle-shaped muscles: for example: in biceps and triceps in our upper arms.
Types of Muscles
- Skeletal Muscles – These are the muscles we use to move around. They cover our skeleton and move our bones. Sometimes they are called striped muscles because they come in long dark and light bands of fibers and look striped. These muscles are voluntary because we control them directly with signals from our brains.
- Smooth Muscles – Smooth muscles are special muscles that don’t connect to bones, but control organs within our body. These muscles work without us having to think about them.
- Cardiac Muscle – This is a special muscle that pumps our heart and blood through our body.
Muscles in Human Body/ Muscular System (मानव शरीर में मासपेशियाँ)
Voluntary (स्वैच्छिक) and Involuntary Muscles (अनैच्छिक मांसपेशियां) :
- Voluntary muscles (स्वैच्छिक मांसपेशियां): These muscles are the ones that we can control. Most of them move our bones around. If we want to run, walk, ride a bike, wave our arms around, it is our voluntary muscles which move our arms, legs and body around. But these muscles can’t do that unless your brain sends the right muscles the messages to ‘contract’ or ‘relax’.
- Involuntary muscles (अनैच्छिक मांसपेशियां): These don’t need us to think about moving them. Some examples are:
- The muscles in our heart, which keep blood pumping round our body.
- The muscles in our digestive system which move food down to our stomach and keep moving it along our bowel until all the goodness that our body needs is taken out. Then these muscles work to push the waste that is left over out of our body.
- The tiny muscles at the bottom of the hairs on our arms which make our hairs stand up when we feel cold, or suddenly feel scared.
Tendons :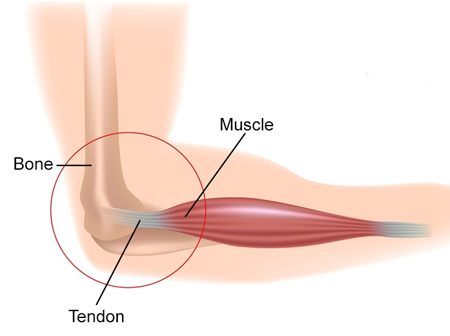
Tendons connect muscles to bones. Tendons help form a connection between soft contracting muscle cells to hard bone cells.
Energy in Muscles :
- Muscles get most of their energy from glucose. Glucose is made from several types of carbohydrates such as sucrose (which is usually called sugar), lactose (from milk) or fructose (from fruits).
- When muscles need to get energy from glucose they do this by changing the glucose into other chemicals such as water and carbon dioxide which releases the energy. They use the oxygen being carried in the blood to help them do this.
Hurting or Exhausting of Muscles:-
- If someone exercise too long, he can get a build-up of chemicals like lactic acid in his muscles, and this can cause it to tighten up and pain.
- Sweating and not drinking enough on a hot day may cause muscle cramp.
- Strains can happen when muscles are stretched too far. Some of the muscle fibers can be torn and there can be bruising inside the muscle.
Disease regarding muscles:
Polio : It is a virus that attacks the spinal cord. The brain can’t send messages to the muscles and they stop working.
Muscles in Human Body/ Muscular System (मानव शरीर में मासपेशियाँ)
Important Facts about Muscular System for Competitive Exams:
- 50% weight of human body is due to weight of Muscles.
- The human body has approximate – 650 muscles.
- Muscles fatigue (थकान), pain or crimping occurs due to deposition of – Lactic Acid.
- Tendons connect muscles to bones
- The three different types of muscle are cardiac muscles, skeletal muscles and smooth muscles.
- The cardiac muscles are muscle tissue found in the walls of the human heart.
- The skeletal muscles are generally attached to bones, like the bicep muscle or the calf muscle.
- The smooth muscles are found in organs that are hallow, like the stomach and bladder.
- The human muscular system contains both voluntary muscles and involuntary muscles.
- A voluntary muscle is one you can control, like using your arms to pick up a box.
- An involuntary muscle is one you cannot control, like your heart beating to pump blood throughout your body.
- The largest muscle in the human body is the Gluteus Maximus, located in the human buttocks. It is also called Hip’s Muscles.
- The smallest and weakest muscle is in our ear and is called the Stapedius. It is attached to the smallest bone in the body, the stapes.
- Our longest muscle is the Sartorius. It runs from the hip to the knee and helps us bend the knee and twist our leg.
- Masseters is the strongest muscle is in our jaw and is used for chewing.
- The least used muscle in the muscular system is in the lower back, it’s the Lumbar Multifidus.
- The most active muscle in the muscular system is the heart. It pumps blood 24 hours day, never gets tired and can beat over 3 billion times in lifetime.
- It takes 17 muscles to smile and 43 muscles to frown. All the more reason to smile instead of frown.
- As the human body ages, the body’s overall muscle mass starts to decrease.
For More:
If you like and think that topic “Muscles in Human Body/ Muscular System (मानव शरीर में मासपेशियाँ)” was helpful for you, Please comment us. Your comments/suggestions would be greatly appreciated. Thank you to be here. Regards – Team SukRaj Classes.