Lungs and The Respiratory System (फेफड़े और श्वसन प्रणाली)
Biology Science topic- “Lungs and The Respiratory System (फेफड़े और श्वसन प्रणाली)”, is important for all competitive exams like: SSC CGL, SSC CHSL, RRB NTPC, UPSC and other state civil services exams. In these exams, almost 4-5 questions are coming from Biology. Let’s start the topic – Lungs and The Respiratory System (फेफड़े और श्वसन प्रणाली) in Human body:
Lungs and The Respiratory System
(फेफड़े और श्वसन प्रणाली)
1. Lungs (फेफड़े) in Human Body:
The lungs are the main component of the human body’s respiratory system. They look a lot like sponges and located on either side of the chest (Thorax).
{Thorax– Thoracic cavity of the chest}
- We have two lungs. The right lung is made up of three lobes. The left lung has only two lobes to make room for our heart. The lung on our left is a bit smaller than the lung on the right because it has to make room for our heart to fit in our chest too. The lungs and the heart need to be close together because they work together.
- Our rib cage goes around our lungs and heart to protect them from damage. Our ribs also move when we breathe in and out.
- Below our lungs is the diaphragm. This is a big muscle that works with our lungs to get air in (inhale – सांस लेना) and out (exhale- सांस छोड़ना).
- We could not take in the oxygen if we didn’t have lungs. We also need to breathe out carbon dioxide into the air. Carbon dioxide is made when our bodies use oxygen and other nutrients in our food to give us energy.
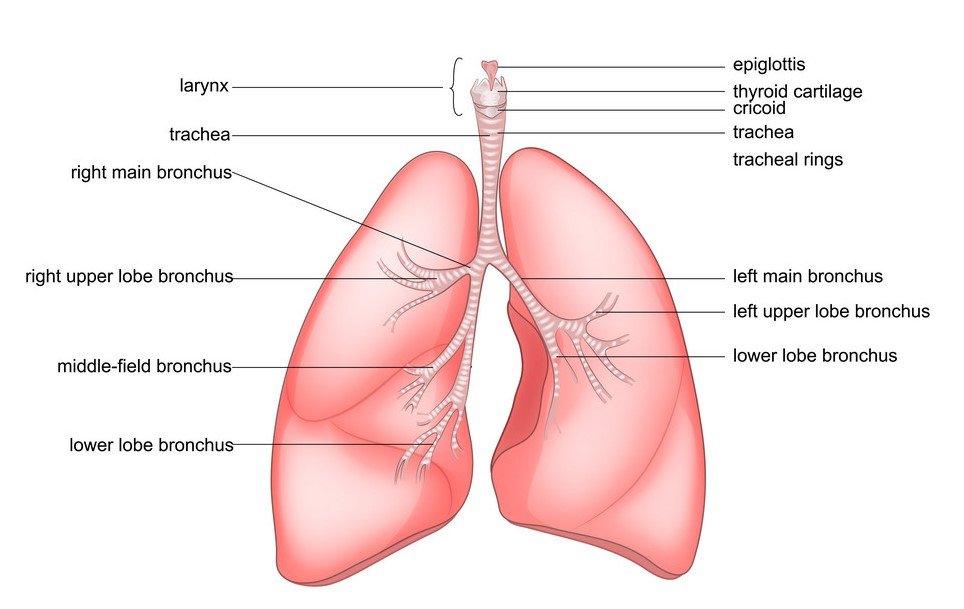
Lung anatomy and Working Process
- The lungs begin at the bottom of our Trachea(windpipe). The trachea is a tube that carries the air in and out of our lungs.
- Each lung has a tube called a bronchus that connects to the trachea. The trachea (windpipe) conducts inhaled air into the lungs through its tubular branches, called Bronchi and this look like tree called the Bronchial Tree.
- The bronchi then divide into smaller and smaller branches which are called –Bronchioles. Like the branches of a tree, these tiny tubes stretch out into every part of our lungs. Some of them are so tiny that they have the thickness of a hair. We have almost 30,000 bronchioles in each lung.
- The bronchioles eventually end in clusters of air sacs called Alveoli. They look like tiny grape bunches or very tiny balloons. There are about 600 million alveoli in our lungs.
- In the alveoli, oxygen from the air is absorbed into the blood. As a waste product of metabolism, Carbon dioxide travels from the blood to the alveoli, where it can be exhaled. The small bubble shapes of the alveoli give our lungs a surprising amount of surface area — equivalent to the size of a tennis court.
- Between the alveoli there is a thin layer of cells called the Interstitium, which contains blood vessels and cells that support the alveoli.
- The lungs are covered by a thin tissue layer called the Pleura.
For More:
Important Facts about Lungs for competitive exams
- The lungs are the main component of the human body’s respiratory system.
- The study of lungs and disorders of the lungs is known as Pulmonology, and one who studies pulmonology is called a Pulmonologist.
- The lungs are covered by a thin tissue layer called the Pleura.
- Infection and Inflammation (सूजन) in lungs due to – Pleurisy disease.
- Unit of lungs – called Alveoli which increase the surface area of lungs, up to 90 meter square where gaseous exchange takes place.
- The lungs are in the thoracic cavity of the human chest.
- The human lungs are what bring oxygenated blood to the heart and remove carbon dioxide from the bloodstream.
- The human lungs are party of the lower respiratory tract.
- Blood purification takes place in Lungs whereas blood filtration takes place in Kidney.
- An average, healthy human will breathe about 2,900 gallons of air every 24 hours.
- The diaphragm (thin skeletal muscle) is what our lungs use to inhale and exhale air.
- A human has two lungs, the left lung and the right lung.
- The left lung is slightly smaller than the right lung to make room for the human heart.
- The right lung has three lobes, the upper lobe, middle lobe and lower lobe.
- The left lung has two lobs, the upper lobe and lower lobe.
- A few examples of lung disease are Asthma, Bronchitis, Emphysema, Lung cancer and Pneumonia.
- Smoking is the number one cause of lung cancer and lung cancer is one of the leading causes of death worldwide.
2. The Respiratory System (श्वसन प्रणाली)
The lungs are the main part of the respiratory system. This system is divided into two tracts: The upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract.
The upper respiratory tract includes:
- Mouth and nose: Air enters and leaves the lungs through the mouth and nostrils of the nose.
- Nasal cavity: Air passes from the nose into the nasal cavity, and then the lungs.
- Throat (pharynx): Air from the mouth is sent to the lungs via the throat.
- Voice box (larynx): This part of the throat helps air to pass into the lungs and keeps out food and drink.
The lower respiratory tract includes:
- Lungs and Its Parts- Trachea (windpipe), Bronchi, Bronchioles, Alveoli
Other parts of the respiratory system help our lungs to expand and contract as we breathe. These include the ribs around the lungs and the dome-shaped diaphragm muscle below them.
WHAT IS RESPIRATION?
Respiration is made up of two phases called inspiration and expiration: We inhale (breathe in) oxygen during inspiration. We exhale (breathe out) carbon dioxide during expiration.
Process of Breathing :
When we breathe, air comes down from our nose or mouth through the trachea or windpipe, into two large tubes called the bronchi.
There are Main two process takes place in Respiration process:
1) Breathing in (Inhale) 2) Breathing out (Exhale).
Breathing in (Inhale):
- When we inhale, or breathe in, the air goes in through our nose or mouth. Little hairs called Cilia inside our nostrils catch tiny particles of dust. If they don’t catch all of them, there are more cilia and mucus inside your trachea, which trap the dust and stop it from getting into our lungs.
- Our diaphragm flattens out (contracts), our rib-cage lifts and the air goes through all the little branches in our lungs to fill up the air sacs, or alveoli.
- Oxygen goes through the walls of the alveoli. Each alveolus is covered by a net of tiny blood vessels called capillaries. Oxygen and carbon dioxide exchange happens here. In these capillaries, the oxygen enters the red blood cells in each tiny blood vessel. The blood carries the oxygen to the heart. The heart pumps all the oxygen-carrying blood to every cell in the body.
Breathing out (Exhale)
- As each red blood cell empties its load of oxygen, it picks up carbon dioxide from the cells and heads back to the lungs.
- The carbon dioxide is carried by the red blood cells in the lungs’ capillaries to the alveoli, where it is emptied into the air that leaves the body when we breathe out.
- As we exhale, or breathe out, the diaphragm relaxes, muscles between the ribs relax and air is pushed out of the lungs.
- This air then goes up through all the bronchioles, up the bronchi, up the trachea and out through the nose or mouth.
Important Facts about Respiratory System for competitive exams:
- The respiratory system is what allows humans to breathe in oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide its mean Respiration is made up of two phases called inspiration and expiration.
- The respiratory system consists of quite a few organs, including the lungs and the diaphragm.
- The maximum capacity of adult human lungs is about 1.5 gallons.
- The human body takes around 17,000 breaths each day or around 2,000 gallons of air.
- The lungs are where the gas exchange happens, oxygen is brought into the body and carbon dioxide is released.
- The diaphragm is the muscle that controls around 80% of the breathing a human does.
- There are two parts to the respiratory system, the upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract.
- The upper respiratory tract is the nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, part of the throat (pharynx) and the larynx (voice box).
- The lower respiratory tract is the trachea, bronchi, right lung, left lung and the diaphragm.
- The respiratory system is the entry point for many viruses, bacteria and fungus.
- Asthma is a disease that is caused by long-term inflammation of the bronchial tubes and it is caused by air pollutants, allergens or genetics.
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, also known as COPD, is a respiratory disease where damage to the lung tissue and alveoli (air sacs) makes it hard to breathe.
- COPD is caused by smoking and breathing in harmful chemicals.
- Pneumonia is a potentially deadly infection of one or both lungs caused by a virus or bacteria. Pneumonia causes fluid build-up in the lungs and prevents your body from getting enough oxygen.
Also Read: Kidney (गुर्दा) in Human Body – Biology Topic
If you like and think that Biology topic on “Lungs anatomy and The Respiratory System (फेफड़े और श्वसन प्रणाली)” is helpful for you, Please comment us. Your comments/suggestions would be greatly appreciated. Thank you to be here. Regards – Team SukRaj Classes.