Human Ear and Hearing System (मानव कान और श्रवणतन्त्र)- Biology
Biology topic – “Human Ear and Hearing System (मानव कान और श्रवणतन्त्र)”, is important for all competitive exams like SSC CGL, SSC CHSL, RRB NTPC, UPSC and other state civil services exams. In these exams, almost 4-5 questions are coming from Biology. Let’s start the topic – Human Ear and Hearing System (मानव कान और श्रवणतन्त्र):
Human Ear and Hearing System
(मानव कान और श्रवणतन्त्र)
- Organ System: Auditory system (sensory nervous system)
- Organ Purpose: Hearing and balancing. (equilibrioception)
- Organ Count: Two: Left-Ear and Right-Ear.
The ear is a hearing organ of the human body. Hearing is how we perceive sound. It’s how our ears take sound waves and turn them into something our brain can understand.
There are three major parts of the ear that help us to hear:
- Outer ear
- Middle ear
- Inner ear

1. The outer ear – The outer ear has three sections:
- The pinna or auricle: this is the part of the ear on the outsides of our head and that we can see. It helps to gather sound and vibrations so that we can hear more sounds.
- The ear canal: This is a tube that helps sound to travel further inside our ear and to get to the next stage of hearing. Cells lining the ear canal make wax to protect the fragile skin in the canal from dirt and water. Ear wax, also called cerumen, is needed and we should not try to remove it.
- The eardrum: The eardrum is a thin sheet that vibrates when the sound hits it. Our eardrum is very sensitive and fragile. We never put anything in our ear as even very soft thing can damage our eardrum.
2. The middle ear –
The middle ear is a small air-filled space on the inside of the eardrum and has three bones in it. These little bones called ossicles that help us to hear. They are called – The hammer (malleus), anvil (incus), and stirrup (stapes). They amplify the sound or make it louder.
- The middle ear helps to transfer sounds from the air to fluid inside the next stage, or inner ear.
- The stirrup (stapes) is the smallest bone in the body.
3. The inner ear –
The inner ear is filled with fluid and has the hearing organ called the cochlea. This organ helps to take the vibrations and translate them into electrical signals for the auditory nerve to send to the brain. It actually uses little hairs (hair cells) that vibrate with the sound waves in the fluid. In this way we “hear” it.
- There are about 17,000 hair cells in each ear.
Note : There are some semi-circular canals (tubes) in our inner ear contain fluid too. They send messages to your brain to help us keep our balance when we move.
Why our ear get blocked up when we have cold ?
Germs like bacteria and viruses can get into our body (like when you have a cold) and they can go inside the middle ear (space behind the ear drum). A middle ear infection is called otitis media. 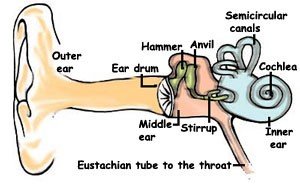
When we have a cold, our Eustachian tube can get blocked up. This tube is between our middle ear and the back of our nose and throat. The Eustachian tube allows air to move in and out of your middle ear to stop pressure building up.
Whenever we have been on a plane or a fairground ride, we feel our ears “pop (Closed)” because of the Eustachian tube doing its job.
Little kids can get ear infections more often than bigger people, because their Eustachian tubes are much smaller and can block up more often.
Why we have two ears?
Having two ears helps us to determine the direction of sound. Our brain is smart enough to figure out that if sound hits one ear just before the other and is slightly louder then that’s the direction the sound came from. Having an ear on each side of our head also helps us to hear well.
Why do we get dizzy (सिर चकराना)?
The brain takes in a number of signals from our body to keep it balanced. One of them is from the fluid in the inner ear. The brain can tell a lot by how the fluid in our ear is moving or tilted. The brain also uses our eyes and sense of touch to tell it about our balance and position. When we spin really fast and then stop, the fluid in our ear is still spinning, but our eyes and body have stopped moving. Our brain gets confused for a bit and we feel dizzy.
In old age, why we get hearing problem ?
The hair cells in our inner ear can become damaged as we get older, so the messages going to our brain are not as clear. That why we may need to talk more clearly to our grandparents and stand where they can see our face when we are speaking.
The Frequency of Sound:
We can hear sound within a certain frequency range of around 20 Hz on the low end and 20,000 Hz on the high end. Some animals have different ranges. For example: Dolphins can’t hear sounds as low as we can, but can hear high sounds of over 100,000 Hz. Dogs and cats can hear much higher pitched sounds than we can.
For More:
Important Facts about Human Ear for competitive Exams:
- The ear has two main functions, and they are hearing and balance.
- The ear transmits sound waves to the brain, allowing us to hear sounds.
- The ear allows us to hear by converting sound waves into nerve impulses that are sent to and interrupted by the brain.
- The ear allows us to feel the effects of gravity and acceleration, helping you keep your balance.
- There are three parts of the human ear, and they are the outer ear, middle ear and inner ear.
- The outer ear is the external visible part on the exterior of the human body.
- The middle ear is between both the outer ear and the inner ear.
- The inner ear is found in the bony labyrinth, which is a complex cavity in the temporal bone.
- Earwax (cerumen) is a waxy substance that the ear secretes for protection, cleaning and lubrication.
- The smallest bone in the human body is found in the ear, and it’s called as Stapes.
- Sounds that are higher than 85 dB (decibels) can damage our hearing.
- Hearing loss is defined as having partial to a complete inability to hear.
- Hearing loss is rated by degrees and there are different 7 degrees of hearing loss.
- The seven degrees of hearing loss are normal, slight, mild, moderate, moderately severe, severe and profound.
- Sign language is a process where one uses hand signs and motions to communicate with someone who can’t hear.
If you like and think that Biology topic on “Human Ear and Hearing System (मानव कान और श्रवणतन्त्र)” is helpful for you, Please comment us. Your comments/suggestions would be greatly appreciated. Thank you to be here. Regards – Team SukRaj Classes.