
Genetics/ Heredity (आनुवंशिकता)- Competitive Biology
Biology topic- “Genetics/ Heredity (आनुवंशिकता)”, is important for all competitive exams like CET, SSC CGL, SSC CHSL, RRB NTPC, UPSC and for other state civil services exams. In these exams, almost 4-5 questions are coming from Biology. Let’s Start topic- Genetics/ Heredity (आनुवंशिकता):-
Genetics/ Heredity (आनुवंशिकता)
Genetics is the study of genes and heredity. It may be defined as the study of genes at all levels, including the ways in which they act in the cell and the ways in which they are transmitted from parents to offspring (children).
- Scientists who study genetics are called – Geneticists.
- Gregor Mendel is known as the father of the science of genetics.
Modern genetics focuses on the chemical substance that genes are made of, called deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). For example, Green plants have genes containing the information necessary to synthesize the photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll that gives them their green colour. Chlorophyll is synthesized in an environment containing light because the gene for chlorophyll is expressed only when it interacts with light. If a plant is placed in a dark environment, chlorophyll synthesis stops because the gene is no longer expressed.
So, Heredity may be defined as a biological process whereby a parent passes certain genes onto their children or offspring.
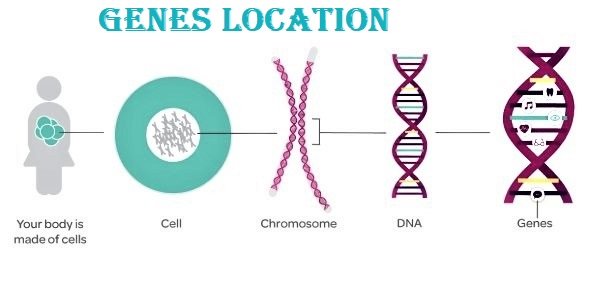
Chromosomes (गुणसूत्र)
- The word “chromosome” comes from the Greek words “chroma”, meaning color, and “soma”, meaning body.
- Chromosomes are tiny structures inside cells made from DNA and protein. The information inside chromosomes tells cells how to function.
- Different chromosomes carry different types of information. For example, one chromosome may contain information on eye color and height while another chromosome may determine blood type.
- Humans have 23 pairs or total 46 chromosomes in each cell. We get 23 chromosomes from our mother and 23 from our father.
- Chromosomes are numbered from 1 to 22 and these are common for both sexes and called Autosomes. There are also two chromosomes that have been given the letters X and Y and termed sex chromosomes. The X chromosome is much larger than the Y chromosome.
- Different organisms have different numbers of chromosomes: For example, a garden pea has 14 chromosomes, an elephant has 56 chromosomes, a horse has 64, a rabbit 44, and a fruit fly has 8 chromosomes.
- Some animals have lots of chromosomes, but much of them have a blank DNA. This blank DNA is called “junk DNA.”
DNA
- All the instructions inside the chromosome is stored in long thin molecule called DNA. DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid.
- This chemical substance – DNA is a made up of something called Nucleotides. There are four different types of nucleotides: A, T, C and G.
- A – Adenine
- T – Thymine
- C – Cytosine
- G – Guanine
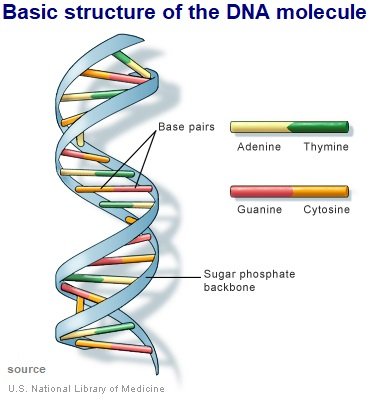
- Different DNAs have different combinations (comes from permutation and combination) of unique codes of chemical bases comprising of A, T, C and G.
- The nucleotides are sometimes referred to as “bases”. These nucleotides are made of phosphate and deoxyribose.
- DNA has a specific shape. This shape is called a double helix. On the outside of the double helix is the backbone which holds the DNA together. There are two sets of backbones that twist together. Between the backbones are the nucleotides represented by the letters A, T, C, and G. A different nucleotide connects to each backbone and then connects to another nucleotide in the center.
- Only certain sets of nucleotides can fit together.
- A only connects with T.
- G only connects with C.
Genes
- Genes are the basic units of heredity which consist of DNA. When we talk about a gene we are referring to a section of DNA
- Genes carry information that determine what characteristics are inherited from an organism’s parents.
- They determine traits (गुण) such as the color of our hair, how tall we are, the color of our eyes and other things like skills and abilities etc.
- Allele: – when we talk about the specific sequence of a gene this is called an allele (युग्म विकल्पी). So everyone has a gene that determines their hair color, one who has black hairs, they have the allele that makes the hair black.
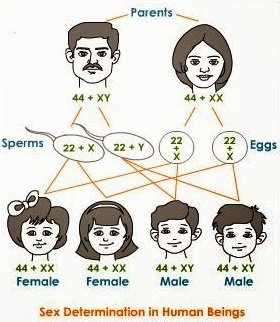
Sex Determination (Males and Females)
Those chromosomes which are involved in the determination of sex of an individual are called sex chromosomes while the other chromosomes are called autosomes.
As we mentioned above, humans have 23 different pairs of chromosomes for a total of 46 chromosomes. We all get 23 chromosomes from our mother and 23 from our father.
A Woman has:-
- 46 chromosomes (44 autosomes + 2 copies of the X chromosome) in her body cells.
- 23 chromosomes (half of total or 22 autosomes + an X chromosome) in her egg cells.
A Man has:-
- 46 chromosomes (44 autosomes + an X and a Y chromosome) in his body cells.
- 23 chromosomes (half of total or 22 autosomes + an X or Y chromosome) in his sperm cells.

When the egg joins with the sperm, the resultant baby has 46 chromosomes with either
XX for female baby
Or
XY for male baby.
As Chromosomes are numbered from 1 to 22 and then an extra pair called the “X/Y” pair. The X/Y pair determines if you are a boy or a girl. Girls have two X chromosomes called the XX, while boys have an X and a Y chromosome called the XY.
Genetics/ Heredity (आनुवंशिकता)- Competitive Biology
Inheritance Theory
(Mendel’s Laws of Genetics):
Mendel was the first scientist who develop a method for predicting the outcome of inheritance patterns.
He performed his work with pea plants (मटर का पौधा), studying seven traits(गुण): Plant height, pod shape, pod color, seed shape, seed color, flower color, and flower location.
During Experiment
- Mendel took pure-line pea plants and cross-pollinated them with other pure-line pea plants. He called these plants the parent generation.
(Note: Over many generations, pea plants pollinate themselves and develop individuals that are homozygous for particular characteristics. These plants are known as pure lines plants.)
 When Mendel crossed pure-line tall plants with pure-line short plants, he discovered that all the plants resulting from this cross were tall. He called this generation the F1 generation (first filial generation).
When Mendel crossed pure-line tall plants with pure-line short plants, he discovered that all the plants resulting from this cross were tall. He called this generation the F1 generation (first filial generation).- Next, Mendel crossed the offspring of the F1 generation tall plants among themselves to produce a new generation called the F2 generation (second filial generation). Among the plants in this generation, Mendel observed that three-fourths (3/4) of the plants were tall and one-fourth (1/4) of the plants were short.
Thus, Mendel conducted similar experiments with the other pea plant traits and he formulated several principles that are known today as Mendel’s laws of genetics. His laws include the following:
- Mendel’s law of dominance: When an organism has two different alleles for a trait, one allele dominates. The dominant characters are expressed when factors are in heterozygous condition.
- Mendel’s law of segregation: This is also known as law of purity of gametes (sperms). It states that when a pair of contrasting factor or gene is brought together in a hybrid, these factors do not blend or mix up but simply associate themselves and remain together and separate at the time of gamete formation.
- Mendel’s law of independent assortment: It states that genes of different characters located in different pairs of chromosomes are independent of one another in this segregation during gamete formation. (These separations occur in the formation of gametes during meiosis).
For More:
Genetics/ Heredity (आनुवंशिकता)- Competitive Biology
Important facts about Genetics/Heredity for Competitive Exams
- Scientists who study genetics are called – Geneticists.
- Father of the science of genetics- Gregor Mendel
- Each gene is a piece of genetic information.
- Some chromosomes are longer than others because they contain more DNA.
- Humans have about 30,000 genes in their 46 chromosomes.
- Chimpanzees in Animal and Potato in vegetables have most nearer chromosome to human being = 48 chromosome.
- Human gets 23 chromosomes from her mother and 23 from his father.
- Carl Wilhelm von Nageli, discovered chromosomes and he was a first person to study about the cell divisions
- DNA stands for Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid.
- About 99.9 % of the DNA of every person on the planet is exactly the same. It’s that 0.1 % that is different that makes us all unique.
- DNA is organized into structures called chromosomes within the cell.
- Girls have two X chromosomes called the XX, while Boys have an X and a Y chromosome called the XY.
- DNA was first isolated and identified by Swiss biologist – Friedrich Meischer.
- DNA molecules have a specific shape called a double helix.
- The double helix structure of DNA was discovered by Dr. James D Watson and Francis Crick.
- Humans share about 90% of genetic material with mice and 98% with chimpanzees.
- Nearly every cell in the human body contains a complete copy of the human genome.
- Some diseases are inherited through genes.
- Mendel’s performed his work with – Pea plants (मटर का पौधा).
Genetics/ Heredity (आनुवंशिकता)- Competitive Biology
If you like and think that Biology topic on “Genetics/ Heredity (आनुवंशिकता)” is helpful for you, Please comment us. Your comments/suggestions would be greatly appreciated. Thank you to be here. Regards – Team SukRaj Classes.

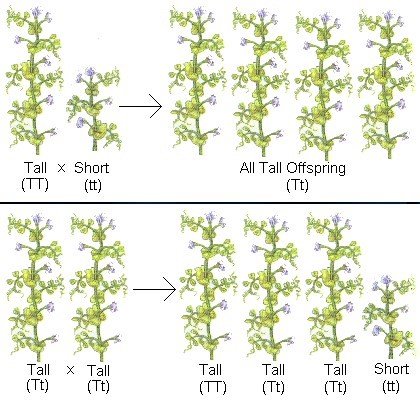 When Mendel crossed pure-line tall plants with pure-line short plants, he discovered that all the plants resulting from this cross were tall. He called this generation the F1 generation (first filial generation).
When Mendel crossed pure-line tall plants with pure-line short plants, he discovered that all the plants resulting from this cross were tall. He called this generation the F1 generation (first filial generation).



