Acids, Bases, Salts and PH Indicators – Competitive Chemistry
Concept of – “Acids, Bases, Salts and PH Indicators – Competitive Chemistry” is important for all competitive exams like CET- Common eligibility Test, SSC CGL, SSC CHSL, RRB NTPC, UPSC and other state PCS exams. In these exams, almost 4-5 questions are coming from Chemistry. Lets start the Topic – Acids, Bases, Salts and PH Indicators – Competitive Chemistry.
Properties of Acids, Bases, Salts and PH Indicators
ACID :
- Acid is a substance which produces hydrogen ions (H+) in aqueous solution e.g. HCL (H+ Cl-).
- An acid is a chemical substance that has a sour taste.
- Many food items have (such as lemons, curd, vinegar and orange) taste sour because of the presence of acid in them.
- Examples of strong acids are: hydrochloric acid, sulphuric acid, nitric acid etc.
- Examples of Weak Acid are: Acetic acid, formic acid, carbonic acid etc.
Natural Acids: These are obtained from natural sources such as fruits and animal products. For e.g. lactic, citric, and tartaric acid etc.
Mineral Acids: Mineral acids are acids prepared from minerals. For example, Hydrochloric acid (HCL), Sulphuric acid (H2SO4), and Nitric acid (HNO3) etc.
Uses of Acids:
- Hydrochloric acid (HCL) present in our stomach helps in the digestion of food.
- Vitamin C or ascorbic acid gives the needed nutrients for body.
- Carbonic acid is used in making carbonated beverages and fertilizers.
- Vinegar a preservative, is a dilute form of Acetic acid.
- Sulphuric acid is used in the manufacture of fertilizers, paints, synthetic fibers etc.
- Nitric acid is used in the preparation of Aqua-Regia, used in the purification of precious metals like gold and silver.
- Boric acid is used to wash eyes.
- Phosphoric acid is used in making fertilizers and detergents.
| Sources of the Acid | Name of the Acid |
| Vinegar | Acetic Acid |
| Citrus fruits | Citric Acid |
| Grapes, Tamarind, Gooseberries, Ripe Mangoes. | Tartaric Acid |
| Sour milk | Lactic Acid |
| Apples | Malic Acid |
| Curd | Butyric Acid |
| Tea, Tomatoes, Spinach | Oxalic Acid |
| Red-Ants and Bees | Formic Acid |
| Proteins | Amino Acids |
| Amla, Guava, oranges | Ascorbic Acid |
BASE :
- Base is a substance which produces Hydroxide ion (OH-) in aqueous solution e.g. sodium hydroxide and ammonium hydroxide etc.
- Bases are bitter in taste and soapy to touch.
- Bases are found in different substances such as bleach, ammonia, washing powder and soap.
- Bases are also called Alkaline.
- All alkalis are bases but all bases are not alkalis.
Note: – Neutral Substance is any substance which is neither acidic nor basic in nature.
SALT :
- When acidic and basic solutions are mixed in proper proportion, they lose their own nature and a new product – Salt is formed.
- Salts are the ionic compounds which are produced after the neutralization reaction between acid and base.
- Salts are electrically neutral.
- A salt may be acidic, basic or neutral in nature.
- Neutral Salt: Salts produced because of reaction between a strong acid and strong base are neutral in nature. The pH value of such salts is equal to 7, i.e. neutral.
- Acidic Salts: Salts which are formed after the reaction between a strong acid and weak base are called Acidic salts. The pH value of acidic salt is lower than 7.
- Basic Salts: Salts which are formed after the reaction between a weak acid and strong base are called Basic Salts.
- There are number of salts but sodium chloride is the most common among them.
- Sodium chloride is also known as table salt or common salt. Sodium chloride is used to enhance the taste of food.
- Most of the salts are crystalline solid.
- Salts may be transparent or opaque.
- Most of the salts are soluble in water.
- Solution of the salts conducts electricity in their molten state also.
- The salt may be salty, sour, sweet, bitter and umami (savoury).
- Neutral salts are odourless.
- Salts can be colourless or coloured.
Uses of Salts:
- Sodium-Chloride is used in the manufacture of chlorine, caustic soda, washing soda and baking soda.
- Ammonium salts are used as fertilizers.
- Potassium-Nitrate is used in the manufacture of gun powder and fire-works.
- Silver-Bromide is used in photography.
- Potassium-Chlorate is used in the match industry.
- Aluminum-Sulphate is used in preparing alums.
INDICATORS:
Special type of substances are used to test whether a substance is acidic or basic. These substances are known as indicators. 
- The indicators change their colour when added to a solution containing an acidic or a basic substance. Turmeric, China rose petals (Gudhal) and Litmus are some natural indicators. Natural indicators the indicators that occur in nature.
- We cannot taste every object and find its nature. Therefore, we use indicators.
- Acid turns blue litmus red and Base turns red litmus blue.
Acid Rain:
When the rain water has increased amounts of acids in it, it is called Acid Rain.
- When pH of rain water is less than 5.6, it is called acid rain.
- The main constituents of acid rain are Sulphuric Acid and Nitric Acid.
- The acid rain is formed because of the presence of air pollutants such as Nitrogen dioxide, Carbon dioxide and Sulphur dioxide in the air.
- These pollutants mix with the rainwater and form acids such as Nitric acid, Sulphuric acid and Carbonic acid respectively.
- The acid rain in severely affect the vegetation, animal life and even buildings of the region where it falls.
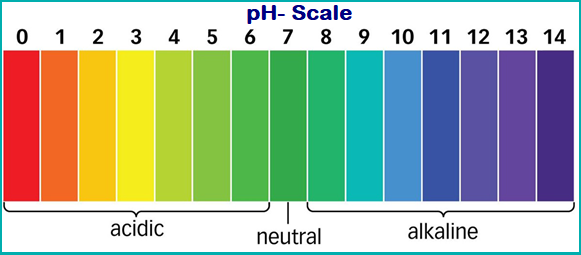
PH Scale and Its Facts:
A scale for measuring hydrogen ion concentration (or strength of acid) in a solution, called pH scale.
- The measure of acidity or basic nature of a substance can be determined by its pH value.
- pH scale was discovered by P.L Sorenson.
- The full form of pH is Potential of Hydrogen.
- The pH value is generally determined by using pH strips or solutions.
- The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14.
- The pH of a neutral solution is 7.
- Values less than 7 on the pH scale represent an acidic solution.
- pH value increases from 7 to 14, it represents a basic solution (increase in OH ion concentration).
Substance PH Value
- Stomach acid 1.7
- Lemon juice 2.2
- Vinegar 2.9 (2.4 – 3.4)
- Soda 3.0
- Wine 3.5 (2.8-3.8)
- Beer 4.0-5.0
- Coffee, black 5.0 (4.5-5.5)
- Urine 5.5-7.5
- Saliva 6.5-7.5
- Milk 6.9
- Pure water 7.0
- Tears 7.4
- Blood 7.3 to 7.5
- Seawater 8.5
- Milk of magnesia 10.5
- Ammonia solution 12.5
Buffer Solutions:
The solutions which resist the change in its PH value on an addition of a small amount of acid or base are called buffer solutions.
- Acidic buffer solution has PH value less than 7.
- Basic buffer has PH value greater than 7.
Acids, Bases, Salts and PH Indicators – Competitive Chemistry
For More:
If you like and think that General Science (Chemistry) topic on “Acids, Bases, Salts and PH Indicators – Competitive Chemistry” was helpful for you, Please comment us. Your comments/suggestions would be greatly appreciated. Thank you to be here. Regards – Team SukRaj Classes.